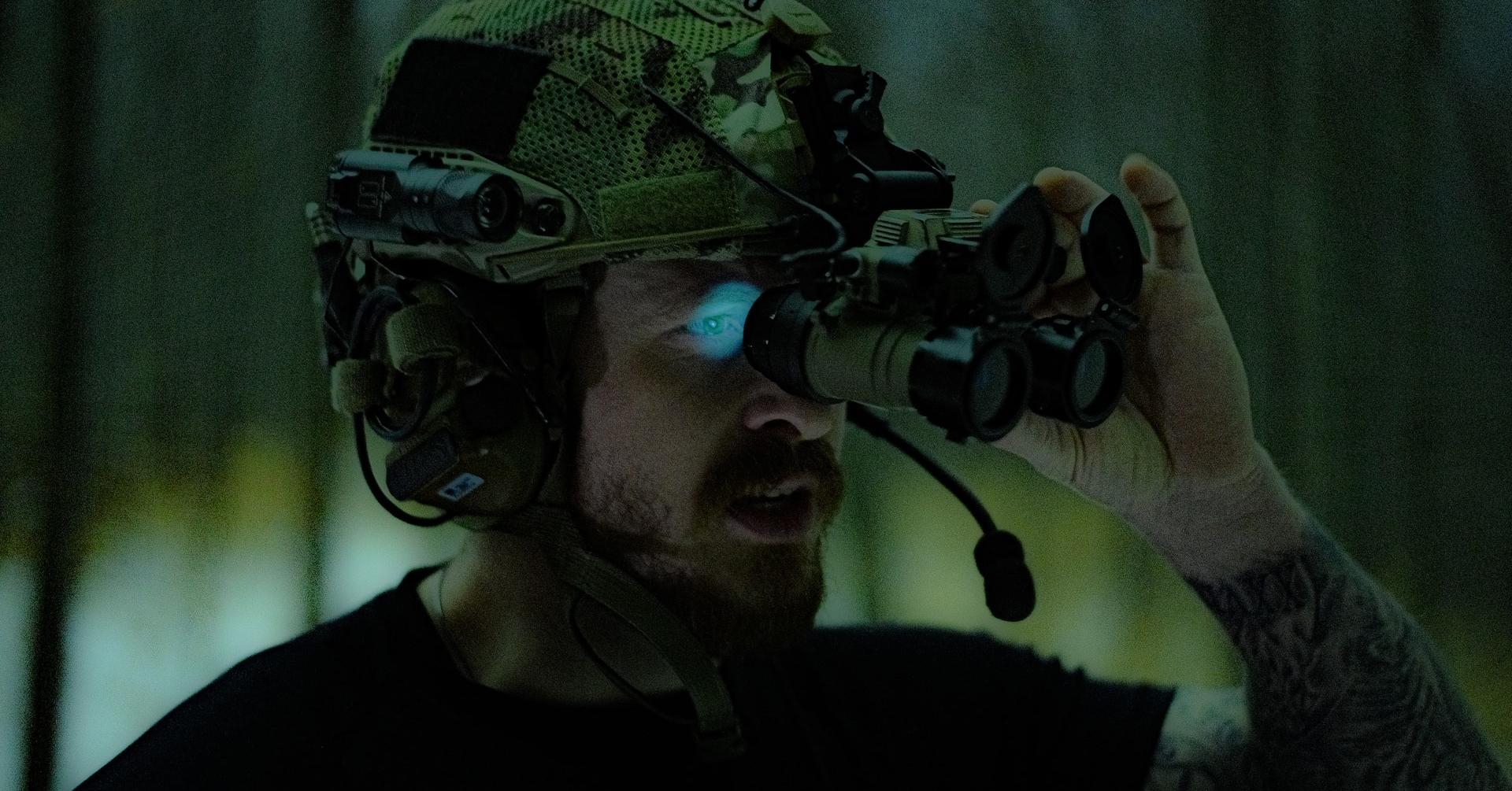
Thermal vision stands as a revolutionary technology, offering a glimpse into aspects of the world beyond the reach of the human eye. This technology captures the heat emitted by objects, transforming it into images that highlight temperature differences. Through this, it reveals hidden environmental patterns, bolsters safety measures, and fuels scientific exploration. Thermal vision uncovers the invisible, shedding light on heat patterns across various scenarios. By doing so, it significantly enriches our comprehension of the complexities surrounding us, opening up new avenues for understanding and interacting with the environment. It is truly a key to unlocking the unseen mysteries of our world.
Thermal vision explained
Thermal imaging, a technology capturing objects’ infrared radiation, unveils the invisible world of heat around us. Invisible to our eyes, this radiation is detected by thermal cameras, which then paint a vivid picture of the world based on temperature differences. These images are displayed in color gradients, with warmer areas highlighted in vibrant yellows, oranges, and reds, and cooler regions in soothing greens and blues. This unique ability to visualize temperature variations in such rich detail opens up new avenues for understanding our environment, providing deep insights into phenomena that would otherwise remain hidden from view.
Five Ways Thermal Vision Deepens Our World Understanding
Let us delve into five ways how thermal vision deepens our understanding of the world.
Environmental monitoring
Thermal vision plays a crucial role in environmental science, enabling researchers to monitor ecosystem health. It can detect changes in surface temperatures, indicating phenomena like forest fires, water pollution, or the presence of invasive species. This information is vital for conservation efforts and understanding the impacts of climate change.
Enhanced safety and security
In the realm of safety and security, thermal imaging is indispensable. It allows for the detection of individuals or objects in complete darkness or through smoke and fog. This capability is essential for law enforcement, search and rescue operations, and border surveillance, providing a level of situational awareness that is unattainable with standard visual equipment.
Medical diagnostics
Thermal vision offers non-invasive methods for medical diagnostics. By visualizing the heat produced by the human body, it can help in identifying inflammation, circulatory issues, or irregular patterns of heat distribution that might indicate disease. This application of thermal imaging is a boon for early detection and patient care, offering a quick and painless assessment tool.
Building and infrastructure inspection
Thermal imaging is a key asset in the maintenance and construction industries. It identifies heat loss in buildings, revealing areas that require improved insulation. Similarly, it can detect overheating components in electrical and mechanical systems, preventing failures before they occur. This not only saves money but also ensures the longevity and safety of infrastructure.
Advancing scientific research
Beyond practical applications, thermal vision contributes to scientific discovery. It allows researchers to study thermal properties of materials, understand the behavior of animals in their natural habitats, and even explore celestial bodies. This breadth of application propels forward our understanding of the natural world, from the minutiae of quantum physics to the vastness of space.
To sum up
Thermal vision is more than just a technological innovation; it is a lens through which we can explore the unseen aspects of our world. By visualizing the invisible spectrum of heat, it provides insights into environmental phenomena, enhances safety and security, aids in medical diagnostics, and supports the maintenance of our built environment. Moreover, it opens new frontiers in scientific research, offering a fresh perspective on the mysteries of the universe. In essence, thermal vision not only deepens our understanding of the world but also expands the boundaries of human perception.