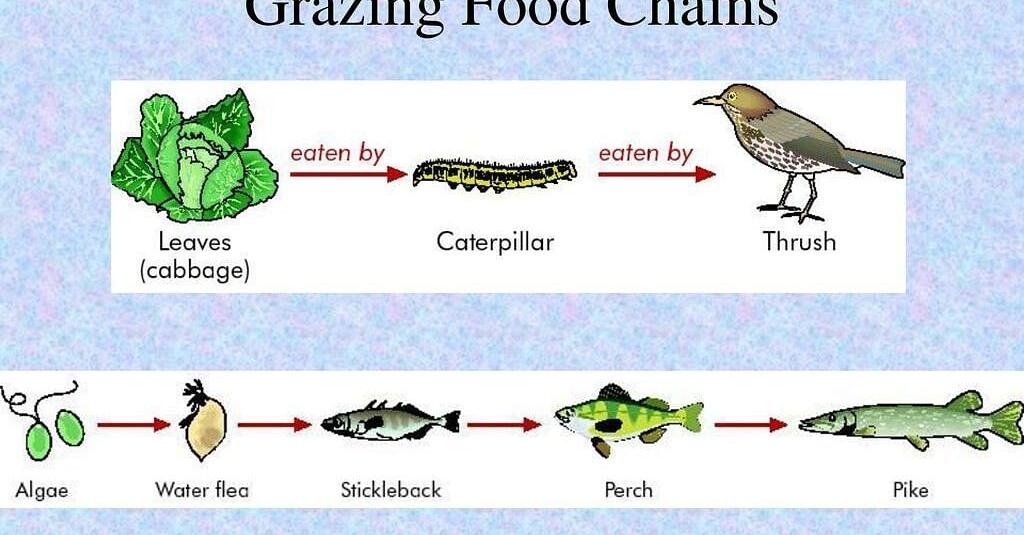
Are you curious to know what is grazing food chain? You have come to the right place as I am going to tell you everything about grazing food chain in a very simple explanation. Without further discussion let’s begin to know what is grazing food chain?
In the intricate web of ecosystems, where every organism plays a unique role, the concept of the grazing food chain takes center stage. A vital link in the natural balance, this chain illustrates the dynamic relationship between herbivores and the primary producers they consume. By delving into the world of the grazing food chain, we can better comprehend the flow of energy and nutrients that sustain life across diverse landscapes.
What Is Grazing Food Chain?
The grazing food chain is a pathway through which energy and nutrients move within an ecosystem. It begins with primary producers, such as plants and algae, which harness sunlight to create energy-rich organic compounds through photosynthesis. These compounds form the foundation of the chain, initiating a sequence of consumption and energy transfer.
Key Players In The Chain:
- Primary Producers: Plants and algae are the initiators of the grazing food chain. They synthesize organic matter using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, creating a source of energy and nutrients for the entire ecosystem.
- Herbivores: Herbivores are the primary consumers in the grazing food chain. These animals feed directly on plants and algae, converting plant matter into energy that fuels their growth and sustenance. Herbivores play a vital role in controlling plant populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Predators and Carnivores: The next link in the chain consists of predators and carnivores. These secondary and tertiary consumers feed on herbivores, regulating their populations and further transferring energy up the food chain.
- Decomposers: Decomposers, including bacteria and fungi, complete the cycle by breaking down the remains of plants, animals, and waste materials. They release nutrients back into the environment, which are then recycled to nourish primary producers, closing the loop of the grazing food chain.
Ecosystem Dynamics And Balance:
The grazing food chain is a fundamental mechanism that regulates energy flow and nutrient cycling within ecosystems. It highlights the interconnectedness of species and their roles in maintaining ecological equilibrium. For instance, an imbalance in herbivore populations can lead to overgrazing and depletion of plant resources, ultimately affecting the entire food chain.
Impact On Biodiversity:
Biodiversity is a key factor in sustaining healthy ecosystems. The grazing food chain contributes to biodiversity by supporting a variety of species, each with its unique adaptations and ecological niches. The presence of herbivores and their interactions with primary producers influence the distribution and diversity of plant species, creating a rich tapestry of life.
Human Influence And Conservation:
Human activities such as deforestation, habitat destruction, and overhunting can disrupt the grazing food chain and lead to cascading effects throughout ecosystems. Conservation efforts are essential to protect and restore these chains, ensuring the sustainability of ecosystems and the services they provide, such as clean water, air, and food.
Conclusion:
The grazing food chain is a testament to the intricate dance of life within ecosystems. From the humble primary producers to the majestic predators, each organism plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. By understanding and appreciating the dynamics of the grazing food chain, we gain insights into the complex relationships that shape the world around us, fostering a deeper connection with the beauty and resilience of the natural world.
You can gather more stuff on Caresclub.
FAQ
What Is Grazing Food Chain And Detritus?
Definition. A grazing food chain is a food chain that starts with green plants as the main source of energy. A detritus food chain is a food chain that starts with the dead remains of organisms as a main source of energy.
What Does A Grazing Food Chain Directly Depend On?
Final Answer: Grazing food chains directly depend on solar radiation.
What Is An Example Of A Grass Food Chain?
Producers i.e. grasses(1st trophic level) are eaten by grasshoppers(2nd trophic level) which are then eaten by frogs (3rd trophic level). The Frogs are then eaten by snakes(4th trophic level). Vultures or eagles(5th trophic level) then prey on these snakes.
What Is Meant By Food Chain In Grassland?
In a Grassland food chain, the initial organisms are grass. They are producers which produces food using solar energy. Insects are primary consumers. They eat plants. They are herbivores.
I Have Covered All The Following Queries And Topics In The Above Article
What Is Grazing Food Chain
What Is Meant By Grazing Food Chain
What Is Mean By Grazing Food Chain
What Is The Grazing Food Chain
What Is Grazing Food Chain And Detritus Food Chain
What Is The Difference Between Grazing And Detritus Food Chain
What Is A Grazing Food Chain
What Is Grazing Food Chain?
What Is Grazing Food Chain
What is a grazing food web in science